GIS based mapping for Agricultural Suitability Assessment
Land Use Mapping: A tool for land policy makers
January 21, 2016
Guide for Mobile Field Survey App to Collect Data
June 17, 2016
Illustrating Agricultural Components
Agricultural suitability assessment, which is the systematical establishment of good, moderate and poor land in order to identify the best use to which land is put, is of importance in the field of agriculture. To achieve sustainable agricultural development, Agricultural suitability assessment should be carried out because it helps to identify the capability of any agricultural land to tolerate the sustainability of agricultural productions for any kind of agricultural practices. Agricultural suitability assessment involves classification and characterization of ecological and biophysical features of lands which helps for the identification of suitable agricultural land use where crops can be cultivated at least environmental and economic costs, leading to the environmentally friendly and economic viability of agricultural production. Agricultural suitability assessment involves the determination of land quality from its features through assessing and grouping different types of land in classes based on their aptitude.
To carry out Agricultural suitability assessment, a large volume of geo-spatial data is required to be captured, processed and displayed cartographically. Geographic Information System (GIS) have become an important tool for acquiring and analyzing such large volume of geospatial data in order to provide answers to questions related to the best locations for different agricultural practices that may contribute to sustainable agricultural production and development.
GIS as a tool in Agricultural suitability assessment
While solving spatial problems related to Agricultural suitability assessment requires proper handling of a large amount of geographical data. Proper handling of such data requires capturing, processing and displaying in such a way that makes meaning to the users for decision-making. GIS as a tool in Agricultural suitability assessment can be applied in the following ways:
- Spatial data capturing: Vast amount of spatial data from different sources such as Remote Sensing (RS), Global Positioning Systems (GPS), field surveying, maps etc., can be captured by GIS. Such data from different sources may include climatic, land use/cover, Digital Elevation Modeling (DEM), Digital Terrine Modeling (DTM), soil properties/distribution, land degradation etc. Integrating such a vast amount of data in the GIS environment increases the accuracy of Agricultural suitability assessment.
- Spatial data analysis: Agricultural suitability assessment is expected to be performed in order to identify the best locations suitable for different agricultural practices. While analyzing spatial data to get the best results, GIS has the capability to enhance satellite image data and geometric correction, classify the land use and soil characteristics for different agricultural practices. Furthermore, it has the ability to analyze DEM in order to understand the geomorphological condition of the agricultural land area. The climatic element such as rainfall and its parameters can be interpolated within the GIS environment in order to evaluate the water availability, run-off, flooding etc. around or within the agricultural land area. These and other similar analysis would enable the analyst to classify agricultural land use into different categories of suitability. Such suitability classes may include:
(a) Highly suitable: this category consists of land without significant limitations to the given type of agricultural practice;
(b) Moderate suitability: this category consists of land with minor limitations to the given type of agricultural practice;
(c) Marginally suitable: this category consists of land with moderate limitations to the given type of agricultural practice;
(d) Currently not suitable: this category consists of land with severe limitations to the given type of agricultural practice but can be improved with some or specific management strategies
(e) Permanently not suitable: this category consists of land with severe limitations to the given type of agricultural practice and would be very difficult to improve.
Spatial calculations of each of these classes to determine the extent of their areas can as well be performed using GIS and increases the efficiency of agricultural decision-making on selecting the best locations for agricultural practice.
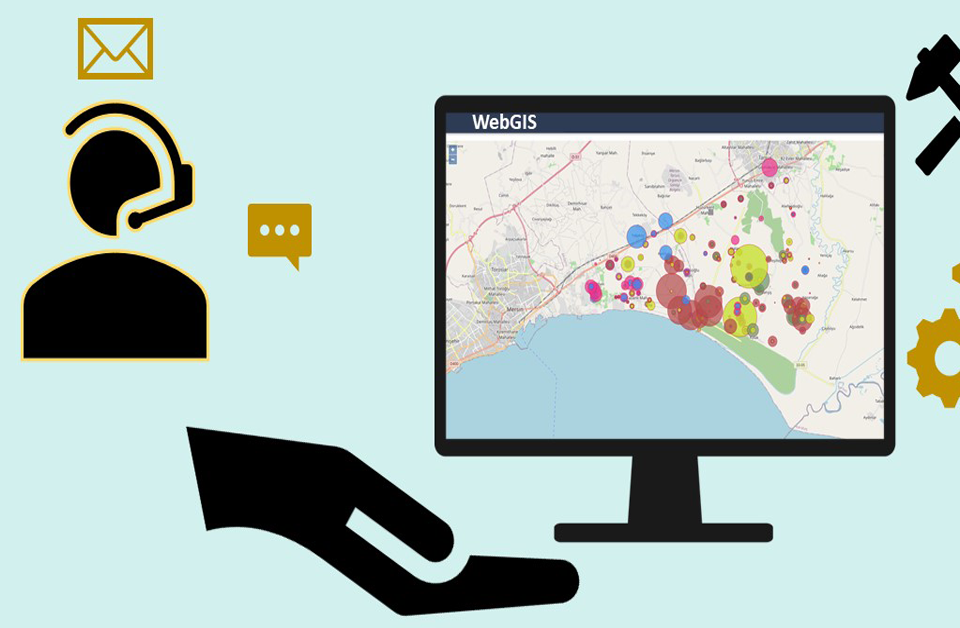
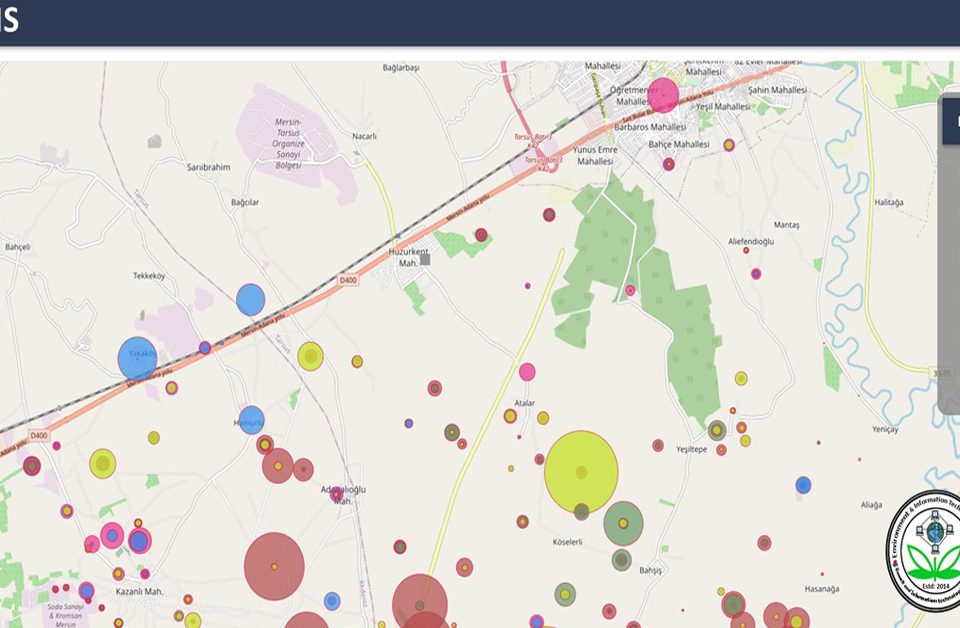
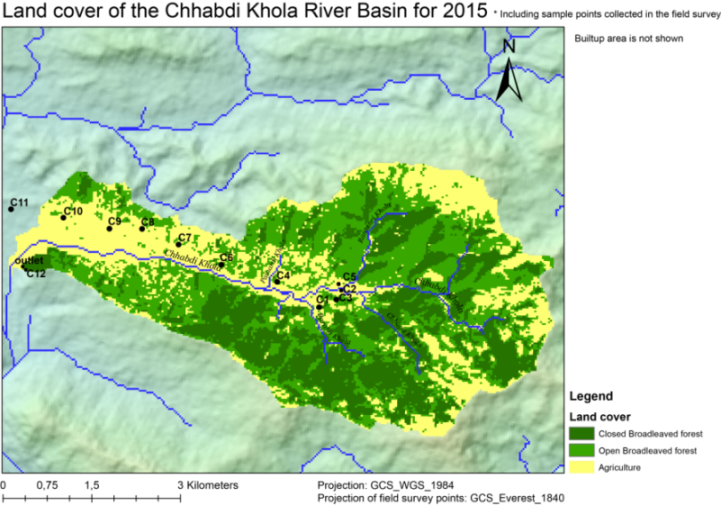
- Spatial information display: for a high level of understanding and interpretation of agricultural suitability assessment by decision-makers and farmers, there is a need for geo-visualization of the results. The beauty of GIS results is its geo-visualization and this enables the decision-makers and farmers to understand, decode and communicate the agricultural suitability effectively. Different agricultural land suitability maps can be overlaid on one another in order to understand the spatial distribution and relationship between them.
Benefits of GIS-based mapping for Agricultural suitability assessment
The role of GIS-based mapping on Agricultural suitability assessment through spatial data capturing, processing and displaying of the final results, has revealed numerous benefits which are not limited to the following:
- Better decision-making on agricultural land suitability: Making a better decision about locations has become an important role of many organizations in different sectors including the agricultural sector. Capturing vast amount of geographic data for analysis leading to a high level of accuracy of the results of agricultural suitability assessment enables farmers and decision-makers to make a better decision on which of the lands are best and least suitable for agricultural uses for sustainable development.
- Cost savings resulting from greater efficiency on agricultural suitability assessment: Application of GIS on Agricultural suitability assessment has revealed greater efficiency, and which in turn has helped to reduce the cost of the assessment. Such costs may include labour cost and time-consuming during data collection and analysis.
- Improved communication on agricultural land suitability: The power of GIS to perform geo-visualization and map overlays has increased the level of understanding, interpreting, and communicating the geo-information related to Agricultural suitability assessment by its users. The language of the map (symbols) can be used to summarize the real-world situation of agricultural land suitability and enables the users (farmers and decision-makers) to communicate effectively among themselves.
- Better Agricultural suitability assessment information keeping: In addition to other functions of GIS such as data capturing, processing and information displays, GIS is used also to store and retrieve data and information. In relation to Agricultural suitability assessment, the results (information) finally produced with the GIS can be stored in the geodatabase of the GIS and can be retrieved at any time such information is needed by farmers, decision-makers, researchers or any other user.
Services for GIS-based mapping for Agricultural suitability assessment
The following services are offered by UIZ in Agricultural suitability assessment using GIS-based mapping:

UIZ Team for Agricultural Survey
- Acquiring vast volume of spatial data such as Remote Sensing satellite images, DEM, DTM, GPS coordinate systems, soil properties and their spatial distribution, etc. from different sources for agricultural suitability assessment;
- Pre-processing of the satellite images and other raster data such as the DTM, DEM, etc. for agricultural suitability assessment;
- Satellite image classification of land use/cover;
- Agricultural suitability assessment based on soil characteristics and distribution, and other factors related to land use in the area;
- Interpreting and professional advice on agricultural land use suitability;
- More as per project requirements.
Call us: +49-30-20679113 or, email: [email protected] to discuss your projects.