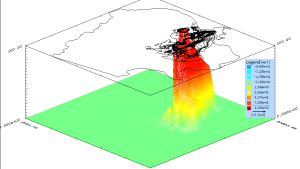
Simulated 3-D groundwater mass scenario
Groundwater modelling
In groundwater systems, the water table is the upper surface of the zone of saturation, the upper surface at which water pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure. Below this groundwater table, the water is under hydrostatic pressure, which is greater than atmospheric pressure. This hydrostatic pressure increases with depth. In general, groundwater is believed to be clean and free from pollution. However, in areas where pollutants are deposited on the ground surface, these pollutants can readily sink into the groundwater, depending upon the permeability of the aquifer. Groundwater can thus be easily polluted by landfills, leaky underground gas tanks, and from overuse of fertilizers and pesticides. Groundwater systems are also easily disturbed by anthropogenic activities such as mining.
Groundwater movement is a believed to be a complex process. UIZ team uses Groundwater Modeling System as a complete program for building and simulating groundwater models. It features 2D and 3D geostatistics, stratigraphic modeling, a unique conceptual and mathematical model approach.
Groundwater models at UIZ
Groundwater models are designed to represent a simplified version of real groundwater scenarios in order to simulate and predict aquifer conditions. UIZ team models broadly as sand tank models, analog models, and mathematical models as per project requirements. For more information about possible modelling services and case study, please contact us.