Project Description
Client
 HEMS, Nepal
HEMS, Nepal
Date
 Ongoing
Ongoing
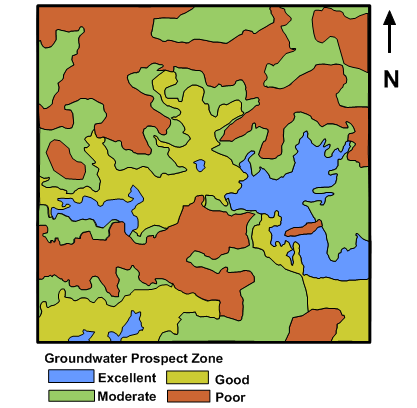
Assessment of drainage and their relative parameters was quantitatively carried out for the Morar river basin, Madhya Pradesh, India. The dendritic type drainage network in the basin showed the homogeneity in texture and lack of structural control in the area. The stream had 1 to 6 order. The drainage density in the area was found to be low which indicated that the area possesses highly permeable soils and low relief.
The study area lies between 2605′ to 26025 N latitude and 78010′ to 78020’E longitude (area 405 km2) from 160 to 360 m average mean sea level (AMSL) and is located in the north eastern part of the Gwalior district in the central India.
Morphometric analysis of Morar River Basin depicted up-to-date information about various factors such as morphological characteristic of the basin and important hydrological parameters such as bifurcation ratio, elongation ratio, drainage density, relief ratio, and circulatory ratio which are responsible for the river basin evaluation, watershed prioritization for soil and water conservation, natural resources management and groundwater potential targeting for efficient planning and management. The results of this project was useful in determining the effect of catchment characteristics such as size, shape, slope of the catchment and distribution of stream network within the catchment.