The Use of Digital Elevation Model in GIS

Application of GIS in Forest Management
May 15, 2020
GIS in Forest Mapping
May 21, 2020What is Digital Elevation Model in GIS?
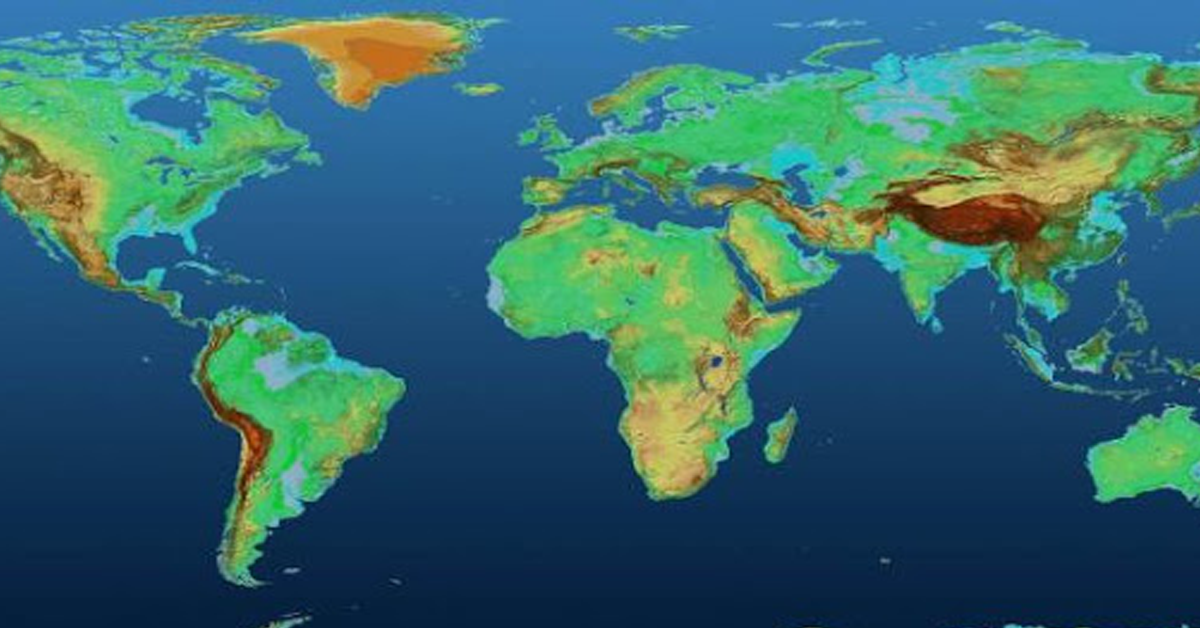
A Digital Elevation Model (DEM) is a specific database that represents to the alleviation of a surface between points of known elevation.
By inserting referred to as elevation data from sources, for example, ground surveys and photogrammetric information catch, a rectangular Digital Elevation Model grid can be made.
GIS software can utilize digital elevation models for 3D surface representation, generating contours, and performing viewshed visibility analysis.
DEMs are useful for landscape analysis. There are a lot further developed and concentrated functions and applications in ArcMap that can be utilized for analysis. This includes, yet is not restricted to, hydrologic analysis, geologic and geomorphic analysis, and landscape improvement.
Advantages of Digital Elevation Model:
1. Evaluating Elevation.
2. Estimating slope and viewpoint.
3. Determining waste systems.
4. Determining the watershed.
5. Terrain stability – Areas inclined to torrential slides
are high slant territories with meagre vegetation,
which is helpful when arranging a parkway or private
region.
6. Soil mapping – DEM’s help with mapping soils
which is an element of elevation (just as geology,
time, and atmosphere).
7. To make a profile diagram from digitized features of
a surface.
Common Uses of DEM:
Extracting territory parameters.
Displaying water stream or mass movement (for
instance, landslides).
Making of alleviation maps. Rendering of 3D
perceptions Creation of physical models (counting
raised help maps).
Correction of aerial photography or satellite imagery.
Decrease (territory correction) of gravity estimations
(gravimetry, physical geodesy).
Territory analysis in geomorphology and physical
geography.
DEM is utilized to decide the qualities of territory, for
example, height anytime, incline and angle.
DEM is additionally used to discover includes on the
territory, for example, waste basins and watersheds,
drainage network and channels and different
landforms.
Sources and Methods to obtain elevation data for DEM in GIS:
There are several methods and sources where we can obtain elevator data for the earth’s surface to create a Digital Elevation Model (DEM) GIS.
Remote sensing is one of them, with all the tools this science can provide, even if this is a satellite or an aircraft. There are more techniques included in remote sensing technology, such as,
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK), which gives us the
enhanced precision of position in the data received
from satellites.
Photogrammetry can also provide information to
create DEM in GIS through aerial surveys which
help us count exact points of the surface from the
taken images.
LiDAR a new surveying method with pulsed laser
light can measure surface height by the reflected
pulses and create 3D DEMs in GIS.
The most usual but nowadays a bit outdated method is the topographic map, created from on-site surveys. With the use of contour lines, we represent the corresponding heights in every position, so we have elevation data which should be digitized to create a DEM GIS. Other tools and methods more advanced are shown below:
Theodolite, a special instrument consisted of a
telescope and placed in vertical and horizontal
planes to measure angles and redeem elevation
data.
Total station, essentially it is a big and electronic
theodolite used for on-site surveying and
construction, equipped with a machine to read
slope and aspect of the ground.
Doppler radar, a mechanism which measures
velocity for objects in distance, emitting a
microwave signal to the target and analysing the
altered frequency when the signal returns.
1. Focus variation, an algorithm used to counter depth
with an optic system. Having depth values for a
whole area we can create the equivalent DEM in
GIS.
2. Range imaging, a whole category of techniques,
usually using a sensor, to measure and show the
distance of various points in a picture from a specific
point.
The image consists of values which represent the
distances. In that way, the result has the form
of DEM in GIS and we can extract elevation data.
3. Structure from motion (SFM), a technique which
combines photogrammetry and range imaging. It
gives us the ability to create a 3D image from a 2D
structure and in that way to estimate slopes of the
ground and produce DEM in GIS.
- For more further information or details regarding Digital Elevation Model please contact UIZ team.