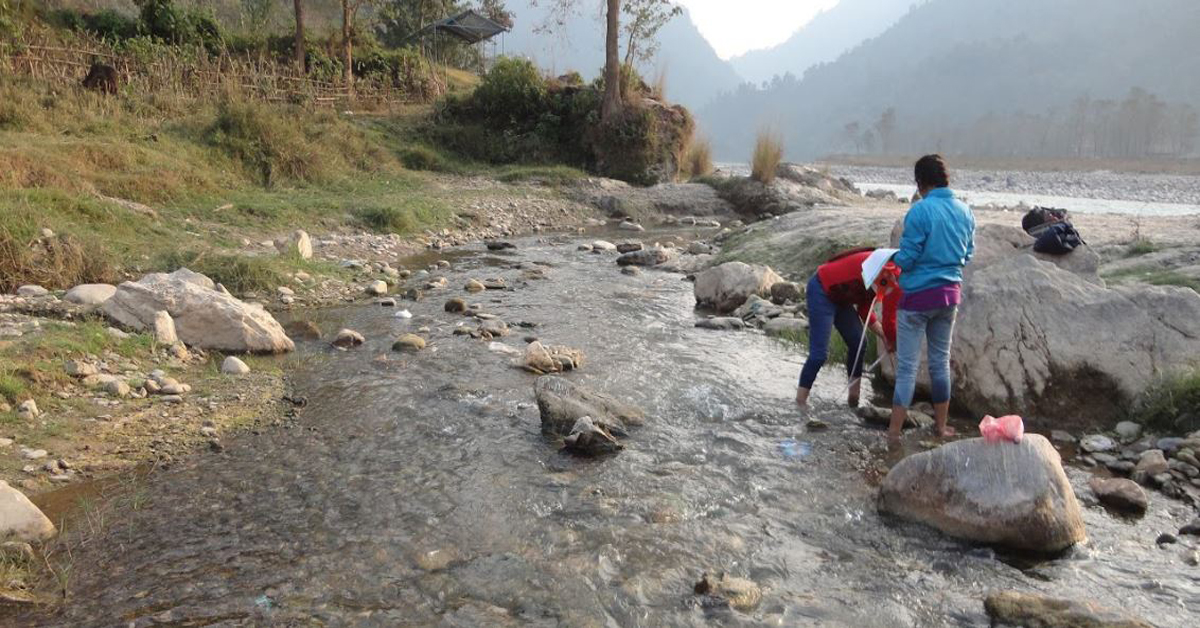
Water Resource Mapping and Methods

Top 5 Free GIS Dataset Sources: Both Raster and Vector Data
April 29, 2020
GIS TO WEB GIS
May 7, 2020GIS is the key program for Water Resource Mapping. It offers extraordinary new apparatuses for assortment, stockpiling, elaboration, the board and show information, re-enactment models and intelligent maps, for the Water Resource Mapping field as well as for different areas of the earth.
We can consolidate in layers a tremendous measure of information, geological and factual and the normal outcome will be great. Bringing in the geological information in the Geographic Information System database will give us the primary layer which comprises the fundamental guide.
Along these lines, we can import information which may contain data, for example, the number of occupants in every region, number of wells, quality parameters, recorded information on withdrawals and so on.
At the point when all the layers are done, the guide is prepared and aside from indicating the imagined information, we can make models to anticipate conceivable future water occasions. Some more applications about GIS water resources are:
- The estimation of the spill depends on the ground slant, the measure of interest in each territory and so forth.
- Formation of maps indicating the precipitation dispersion surface of the beat at which snow is liquefying.
- Speed, bearing, focus and time of water stream for waterways or precipitation overflow.
- Groundwater streams the musicality of drilling, recharges and the degree of the aquifer.
Remote sensing for Water Resource Mapping
Remote sensors offers us the chance to utilize multi-fleeting satellites and the new refreshed Synthetic Aperture Radar sensors (SAR), which permit us to have photos of the earth regardless of whether there are mists or to distinguish water when is stale between developing sea-going plants and timberland shades.
Water uncovered on a superficial level can be recognized utilizing obvious, infrared and radar pictures, while freshwater entering normal bowls needs warm infrared sensors.
With respect to the dirt stickiness, microwave radiometers and radars are the best arrangements though the capacity of groundwater is assessed by gravitational studies. Among the others, with remote detecting we can abuse the accompanying applications:
- Water Resource Mapping identified the evapotranspiration in a zone and thought about the advancement in the years. This procedure may incorporate the information, for example, the water crops used over the scene or the water dissipation during the water system and substantially more information identified with Hydrology.
- Underground Water Resource Mapping, drills and the advancement of water utilization relying upon the withdrawals and energizes.
- Watch the state of ice sheets in the years, making determinations for the degree of waterways, ocean and lakes.
- Decision making to limit the impacts of all the above potential changes.
In addition, remote detecting for Water resource Mapping is these days substantially more helpful and practical. The pictures and maps of the earth we take from the satellites can be utilized for different applications through them and we can send out numerous information. This implies fewer estimations with ordinary techniques and subsequently less exertion, time and cost.
Photogrammetry for Water Resource Mapping
Another strategy to delineate Water Resources is Photogrammetry, the science through which we take photographs straight and sideways to draw a territory and measure the statures of bluffs, structures and so forth.
The benefit of this water resource mapping is that it offers a wide scope of uses with quantitative and subjective data while the information recording requests least time and it is not influenced by the climate.
Photogrammetry is relying upon geodetic estimations and on-location estimations, just as require qualified staff to complete the on-location works and the understanding.
Different Techniques for Water Asset Mapping:
- Quest UAV:
It is a subsection of photogrammetry (the generally known as automatons) offering photographs on a superior scale and time with extraordinary exactness. The upside of little scope influences the image investigation from which we can send out more data than utilizing a satellite.
- LiDAR:
Light Detection A and R It is a sensor which selfishly gauges climatic toxins by discharging a beat laser light on the objective. We use it in water asset mapping because of the sensor’s affectability to water fumes and the mists.
- Shrewd Sensors:
Fixed in that approach to get contributions from the earth and through a calculation to expound the information, expel the commotion and pass the information on. Keen sensors are fundamentally centred around the field of progress and they can distinguish spillages and contrasts in water assets condition extremely quickly.
Water Point Mapping
Water Point Mapping (WPM) is an instrument for observing the circulation and status of water supplies. It gathers information about various viewpoints identified with the water office and overlays this point information with data about populace and authoritative limits.
Water Point Mapping assists with envisioning the spatial dispersion of water supply inclusion and can in this manner be utilized to feature value issues. The data gathered gives bits of knowledge into plans’ manageability levels and the board related parts of water focus.
Water Point Mapping (WPM) can be characterized as an ‘activity whereby the topographical places of all improved water focus in a territory are accumulated notwithstanding the board, specialized and demographic information.
A handheld Global Positioning System (GPS) unit is utilized to record the exact area and estimated height of all water focuses examined; a computerized camera is utilized to catch photos of each water point so as to show the status and states of being and an organized poll is finished to archive fundamental attributes, for example, area, usefulness, classification of water supply, water quality observation, the board issues, possession and water levy instalment.
Every single gathered data is entered into a topographical data framework and connected with accessible segment, managerial, and physical information. The data is at last shown utilizing advanced maps.
How we can Support You With Water Resource Mapping Service
- UIZ Company with years of experience in the field of GIS, Remote Sensing and environmental surveys provides qualified staff drafting projects related to Water Resource Mapping with the best results.
- Contact us for more information about Water resource mapping service