Metadata Management with GIS Contribution

Use of Digital Elevation Model (DEM) in GIS
December 2, 2017
GEO DATA STORING TYPES
April 9, 2018Meaning and Use of Metadata
Metadata Management: It is really strange when new terms are created, as science grows and now we have to deal with metadata. So, metadata is data referred to other data. In other words, Metadata is data of data. i.e. information about data. Yes, this is it! But now let’s explain it. Metadata is a file with informative content about other data. For example, if our primary data are geospatial, videlicet referred to a specific area, then the metadata may refer to who created the area, how big it is etc. Its utility is crucial for acceleration and enhancement when we research something, and to avoid time-consuming and complicated processes.
The separation between the sample data and the metadata is usually hard, as metadata can be also primary data, while primary data can be metadata simultaneously. The interpretation of data depends on the way we see them, in order to decide if we will use them as primary data or metadata.
The reason for creating metadata is hidden back to 1980 when it was widely used in libraries to help librarians find a specific book among so many. Later when the catalogues converted to digital, they kept using the rules of metadata, this time for digital files but keeping the standards of metadata even if they became digital metadata.
Types of Metadata and Usefulness of Metadata Management
A logic sequence drives us to the conclusion that metadata may be an enormous file, so they governed by the need for better metadata management. Over the years, numerous categories of metadata created, in order to categorize and manage them better. There are several types of metadata, divided depending on their use and this is due to better metadata management. The first and main division is about the form and content of metadata, in the categories of descriptive, structural and administrative metadata by NISO. Two more scientists categorized metadata in other sectors as shown in the picture.
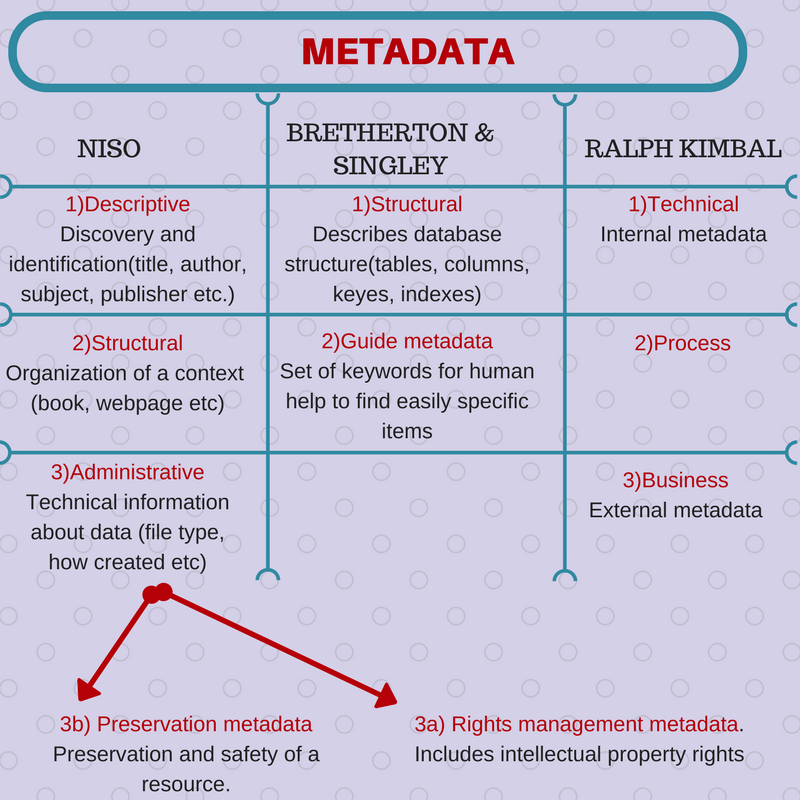
Main categories of metadata
Moreover, there is a division depending on the different disciplines metadata may refer to. For example, we have metadata for museum collections, for websites, for electronic resources etc. There is also another type of metadata, the as named accessibility metadata which consolidate and filter terms and models that recently tagged to a universal framework in order to be easily accessible for educational and researchable reasons, to discover new sources, and apply the right way of metadata management. These data are usually stored and get edited through a database called metadata registry or metadata repository created always to facilitate metadata management.
Last but not least, the fear of losing contents in the future due to the continuous development of science is now anymore past. Metadata management can ensure that electronic files will be stored safely, won’t change and stay useful when new technologies for storing and changing formats discovered. This is the miracle of evolution and better metadata management.
How GIS Contributes to Better Metadata Management?
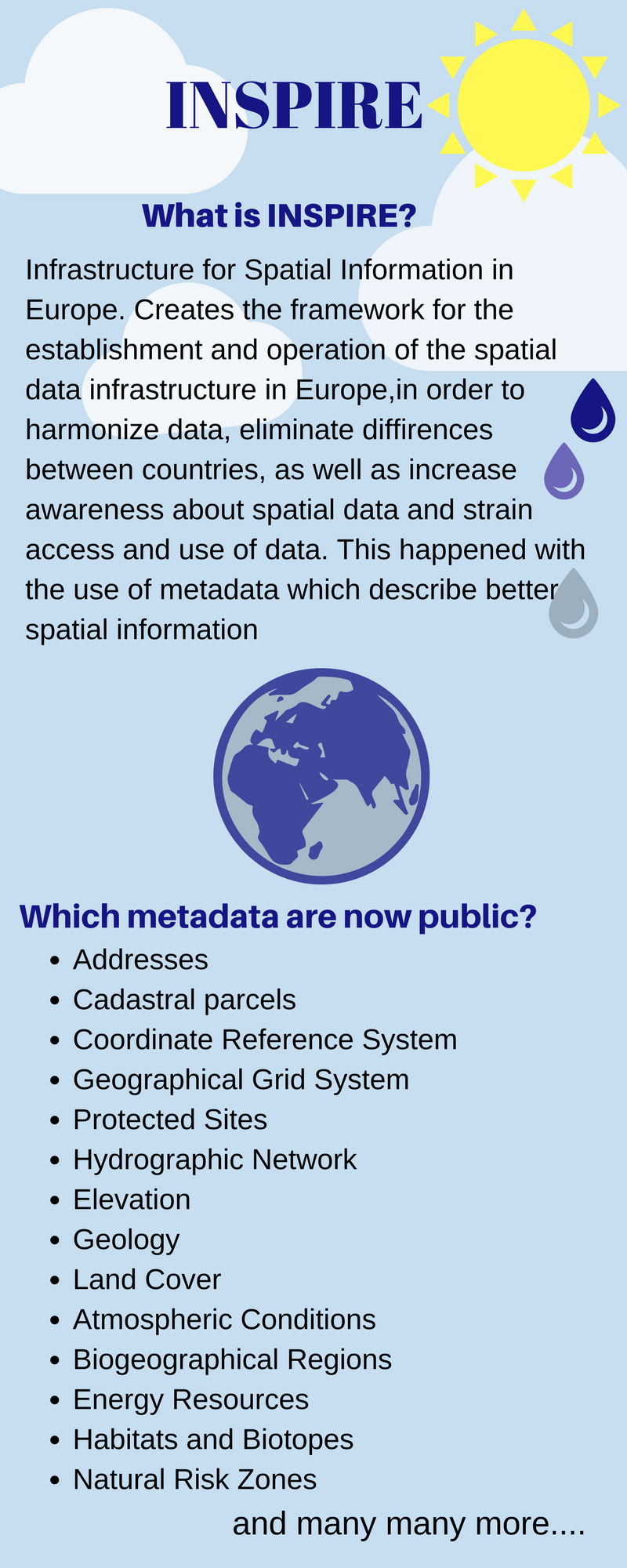
INSPIRE guide.
GIS is a key element for metadata management, providing possibilities of enormous databases and the widely known attribute table with information and characteristics about a specific item. In this situation, the attribute table takes the form of metadata table including the necessary information for identification of data, as provided by INSPIRE guide. In that way, there is efficient metadata management and a clear and concise method to show the results to the user.
Another advantage of metadata management through GIS is that GIS files can be shared easily between organizations and modest users. This process demands strict documentation and archiving of data characteristics and sources, in order to secure data integrity and further metadata management.
Moreover, as it is mentioned above, metadata are enormous records, so GIS provides a large database necessary for the needs of metadata management. It is very crucial to edit and analyze large quantities of spatial information without disturbance or losses may be caused due to lack of space and capabilities of the software. Using GIS, it is guaranteed that such problems won’t occur, and metadata management will roll without issues. Below we can see some advantages of GIS in metadata management, epigraphically:
-
Help edit, analyze, determine and maintain metadata.
-
Help find out the reliability of the data and how current it is.
-
Assist in maintaining data accuracy, as well as verify it.
-
Support the upgrading of the existed metadata.
-
Supports decision making for critical issues such as legal problems, national and environmental disasters etc.
Of course, we shouldn’t forget the importance of the inverse relationship, since metadata management is equally important to the efficient use of GIS. This means that the right metadata management in GIS provides time and cost saving among others. It has been written in another article that collecting data and the sources for GIS are the costliest processes. When metadata take place in the whole process of GIS from the beginning, then creating metadata costs almost nothing. A quick result in emergency situations is one more advantage. For example, official staff facing homeland security demand direct result in enormous and combinational databases which are very hard for an unorganized system. However, the right metadata management provides celerity in GIS.
To conclude, the list of the advantages of GIS in metadata management could be endless but it is practically impossible to mention them all. However, if you need more information about metadata management, GIS software, and their relation, UIZ can explain and answer all your questions. You can reach us at +49-30-20679116 or at UIZ webpage for GIS services.