Watershed Monitoring by GIS

Sources for Geodata Mining
May 3, 2018
Types of Geodata Storing in GIS
May 9, 2018The Role of Watershed
Watershed has many different definitions according to hydrology. The broader and most well-known definition of a watershed describes it as an area where surface runoff and small rivers are flowing to end up in a watershed with the strictest meaning. This means that watershed can describe either the whole area where surface flows take place or the basin itself. There is a whole science behind watersheds which analyze relevant characteristics such as the way the flows behave, ground permeability, basin capacity, and others. Of course, the research about watersheds doesn’t stop here because there is a need not only for knowledge about them but usually we have to deal also with problems created in and around the basin. For example, it is a problem when a watershed has a low water level, or the regional rivers are contaminated because the contamination will enter the basin. The same applies to the ground also. Moreover, monitoring a watershed helps us prevent problems with the natural habitat of plants and animals, manage water quality and supply, drainage deposition and human protection when it is necessary. Below we will see the main factors which affect the watershed and how GIS can help us monitor the case, estimate and prevent difficulties.

The broader watershed includes all the regional small rivers, while the basin is the main river
Water quality monitoring in a watershed
We need to know the quality of water in a watershed because this basin may feed with water a whole city or village. It is crucial though to know that the water is enough to clean to be drinkable. Besides, we must know if it is suitable for swimming over there. There are many cases of people who swam in not very clean water and they had very important consequences in their bodies. It is essential the water of the basin to characterized as a bathing water.
We can have an image of the situation in the watershed with tools and applications provided by GIS with pictures from remote sensing. More specific, GIS allows us to localize where the water of the basin meets the criteria of drinkable water or bathing water etc., and we can easily keep an eye on the pollutants. Another method of GIS, for watershed monitoring, water quality instruments are mounted in several points in the basin and in that way, we have continuous measurements, while in the database we have all the necessary documentation so that to now every time automatically if there is a point which exceeds the foreseen limits.
Presence of factories around the watershed
Another important factor for the right management of the watershed is the presence of factories in the broader area. Factories usually produce liquid waste which is deposited either on the ground or in the nearest river. This means that the consequences are tremendous. GIS again has the tools to provide the necessary data to monitor the area and take the appropriate measures to prevent potential future disasters such as destruction of flora and fauna, overheating water and eutrophication.
First of all, we have to point out in existed maps, the spots around watershed where there is a factory. Digitizing them will make the procedure easier as well as we will have the ability to measure distances from the basin etc. Moreover, we can insert in GIS system data such as the pollutants produced by each factory, how they elaborate their waste or where they deposit it. In this way we will have at the end, collected data for all the closed factories and it will be easier to estimate the existed situation as well as draw conclusions and act where it is required.
Pesticides ended up in a watershed
It is a very common phenomena, the areas around a watershed to be full of fields. And this means that there also exist pesticides. Pesticides have the ability to infiltrate into the ground and the roots of the plant. And they may be healthy for the plants, but they are not for the water. The humidity of the soil draws away from the pesticide from the root and take it to the water’s flow which runs into the watershed. The results are known. Water becomes rich in phosphorus and eutrophication.
GIS in this case, helps us through satellite images and remote sensing to find out where there is excessive existence of chemical components in the ground and through combined data such as the above mentioned about the humidity soil and underground flows, to estimate when the pesticide will enter the basin and how strong will be at that time. Moreover, the maps of GIS are very useful to find the right point where the corresponding method of remediation will take place.
Level of water in the watershed
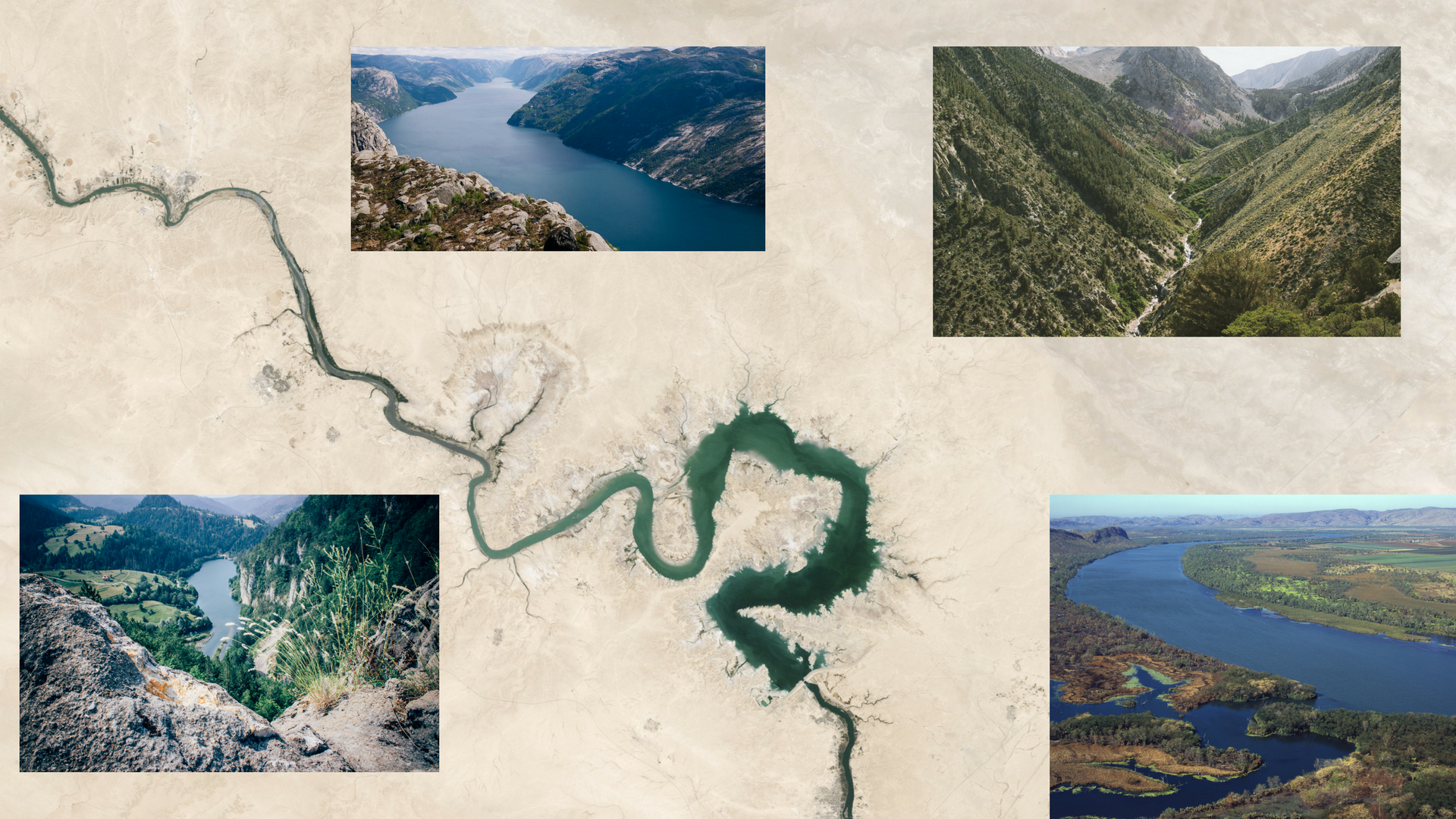

Watershed depicted by remote sensing in the centre and as seen in real from side images
One of the biggest problems generally in the earth is water overexploitation. Watersheds usually are used to irrigate fields, to drill water for various purposes, to supply villages or a city with water etc. But water, especially in a basin is not endless. It is very important to monitor the level of the water in every basin with continuous data and keep a record of them. It is an obligation for us to know all the withdrawals and recharges so that to better manage the area.
In this case, GIS helps us most to keep the records and represent in story maps and 3D maps the evolution of a watershed. It is not about elaborating data, but to analyze the existed situation in comparison with past data, and make decisions about it.
To conclude we can realize how important is a watershed for people, as well as to maintain the balance between ecosystems. GIS is a great tool for this purpose and becomes more and more upgraded to serve people needs.
UIZ masters all the upgraded tools of GIS and is available to implement your projects in the fields of GIS, remote sensing, watershed monitoring etc. For more information, you can call us at +49-30-20679130 or visit our UIZ Company webpage.